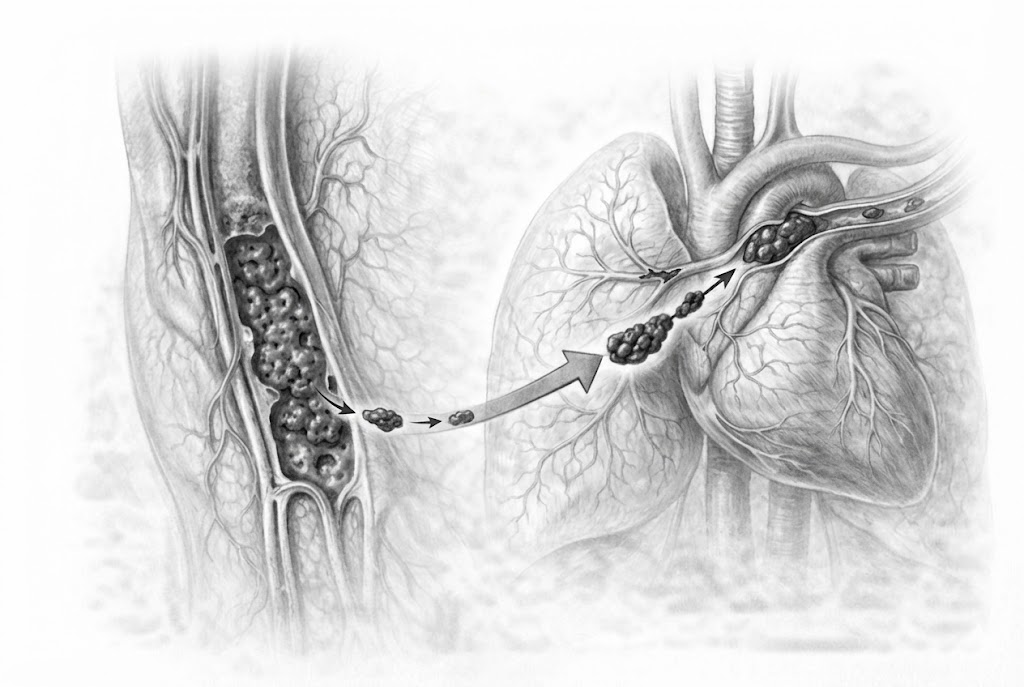
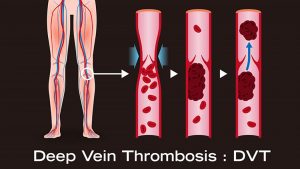
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a circulatory system disorder characterized by a blood clot typically forming in the deep veins of the legs. This clot obstructs blood flow within the vein and, if left untreated, can lead to serious complications. DVT most often occurs in the veins of the calf or thigh but can rarely be seen in the arms as well.
Its most serious complication is pulmonary embolism, which occurs when the clot breaks free and blocks the pulmonary arteries. This condition can be life-threatening and requires immediate intervention.
In Which Situations Does DVT Develop?
Deep vein thrombosis is usually associated with one or more of the following risk factors:
- Prolonged immobility (for example, long airplane or car journeys)
- Major surgical operations (especially orthopedic surgeries)
- Trauma or lower extremity fractures
- Pregnancy and postpartum period
- Hormonal medications (birth control pills, hormone therapies)
- Cancer and certain blood disorders
- Family history of blood clotting
- Obesity and advanced age
In some individuals, genetic clotting disorders (thrombophilia) can also increase the risk of DVT. Therefore, in cases of unexplained thrombosis, advanced genetic tests may be necessary.
What Are the Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis?
DVT may not always present with obvious symptoms. However, the following signs are frequently observed:
- Pain in the calf or thigh area (usually on one side)
- Swelling in the leg, especially in the ankle and calf
- Redness and increased skin temperature
- Discoloration or shininess of the skin
- Increase in leg circumference (difference in diameter)
In some patients, DVT can progress without any symptoms and may directly manifest as pulmonary embolism. Therefore, asymptomatic progression should also be considered in individuals within risk groups.
How Is It Diagnosed?
Deep vein thrombosis is diagnosed through clinical evaluation and imaging methods. In case of suspected DVT, the diagnostic tools used include:
1. Doppler Ultrasonography
It is the most commonly used method. Blood flow within the vessel is measured to determine if there is an obstruction. It is a painless, non-invasive, and reliable method.
2. D-dimer Test
An elevated level of D-dimer, a blood clotting product, in the blood suggests the possibility of DVT. However, it cannot diagnose on its own and should be supported by ultrasound.
3. CT Venography or MR Venography
These can be used in rare cases or when there is suspicion of clots in lower-level vessels. They are particularly preferred for pelvic region thrombosis.
How Is Deep Vein Thrombosis Treated?
Treatment is tailored to the individual based on the location and size of the clot, accompanying diseases, and risk of complications. The aim is to prevent the clot from progressing, prevent it from reaching the lungs, and stop the formation of new clots.
1. Anticoagulant (Blood Thinning) Treatment
Forms the basis of DVT treatment. Types of medications used:
- Low molecular weight heparin (in injection form)
- New generation oral anticoagulants (NOAC/DOAC): Drugs such as rivaroxaban, apixaban
- Warfarin (coumadin): An older treatment option, requires INR monitoring
The treatment duration is generally at least 3 months, but in some cases, it can extend to 6-12 months. The decision for long-term use is made based on the cause of the clot and the patient’s individual risks.

2. Catheter-Assisted Clot Dissolution (Thrombolytic Therapy)
Especially in young patients with extensive (extending to abdominal veins) and newly formed clots, a clot-dissolving drug is administered through a catheter placed inside the vein. This treatment:
- Allows for faster dissolution of the clot
- Reduces long-term damage to vein valves
- Lowers the risk of post-thrombotic syndrome
However, it is not applied to every patient due to the high risk of bleeding. Suitability should be carefully evaluated.
3. Use of Compression Stockings
Recommended especially during the recovery process. It reduces venous pressure in the leg, alleviating edema and pain. It also reduces the risk of post-thrombotic syndrome. It is recommended to wear them for at least 8 hours a day.
4. Surgical Intervention in Advanced Cases
In very rare cases, especially in life-threatening large vessel thrombosis, surgical clot removal (thrombectomy) may be necessary. This procedure is usually performed in specialized centers by experienced surgeons.
Can DVT Be Prevented?
Yes. Some preventive measures can inhibit the development of the disease, especially for people at risk:
- Moving legs and drinking plenty of fluids during long journeys
- Early mobilization after major surgeries
- Use of anticoagulant medications temporarily if necessary
- Regular monitoring during hormone therapies
- Weight control and regular exercise
Deep vein thrombosis is a vascular disease that can progress without symptoms but carries a life-threatening risk. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can both reduce the risk of pulmonary embolism and prevent long-term complications. If symptoms such as swelling, pain, or color changes in the leg are noticed, it is necessary to seek medical attention without delay.