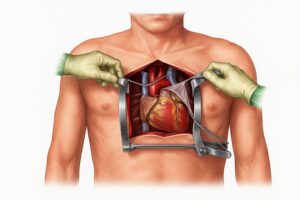
Open heart surgery remains one of the most frequently performed and well-established procedures in modern cardiac surgery. This approach enables a wide range of successful surgical interventions, particularly in cases of valvular heart disease, congenital cardiac anomalies, complex vascular procedures, and advanced coronary artery disease. A key aspect of this technique is the temporary induction of cardiac arrest, with systemic perfusion maintained via a cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) machine.
What is a Heart-Lung Machine and Why is it Used?
During open-heart surgery, the patient is placed on cardiopulmonary bypass, which temporarily assumes the functions of the heart and lungs. The cardiopulmonary bypass machine sustains systemic circulation and oxygen delivery to vital organs during the procedure. Arresting cardiac activity allows the surgeon a bloodless and motionless field for precise access to intracardiac and pericardial structures. Bu sayede son derece hassas ve detaylı müdahaleler mümkün hale gelir.
Upon completion of the surgical repair, the heart is weaned from cardiopulmonary bypass and resumes autonomous circulation. This transition is meticulously monitored, and once stable cardiac rhythm is re-established, the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit for postoperative observation.
Sternotomy: The Incision Technique Used in Open Heart Surgery
The standard approach for chest entry in open-heart surgery is a median sternotomy. Median sternotomy involves a vertical midline incision through the sternum to provide direct access to the thoracic cavity. This technique provides optimal exposure to the entire heart and great vessels. Its comprehensive exposure is particularly advantageous in complex cardiac reconstructions.
Sternotomy facilitates clear visualization of cardiac valves, coronary arteries, major vessels, and the myocardium. This enables precise and safe execution of intricate surgical procedures.
Advantages of Open Heart Surgery
The biggest advantage of this method is that the surgeon can directly access every part of the heart and intervene in all types of complex heart diseases. Advanced procedures such as repairing holes in the heart, replacing or repairing heart valves, removing tumors, and major vascular changes can be successfully performed with open heart surgery.
Additionally, this technique has been applied worldwide for many years and has the most experience and database in surgical literature. This allows for the prediction of complications in advance and the completion of the surgery with a high success rate.
Things to Consider and Recovery Process
Recovery Process and Physical Limitations
Although open heart surgery is a safe technique, there are some disadvantages related to sternotomy. Cutting the breastbone requires approximately 2-3 weeks of healing time for this bone to fuse back together after surgery. During this process, it is extremely important for the patient to be careful with physical movements.
Especially actions like heavy lifting, bending forward, or getting up from bed with support can make bone healing difficult and delay the recovery process. Positions and movement restrictions recommended by the surgeon and physiotherapist must be strictly followed.
Infection Risk and Follow-up Process
During the recovery period, it is also necessary to pay attention to hygiene rules to prevent infection risk, regular medication use, and proper nutrition. After discharge from the hospital, it is critical to attend regular check-up examinations to ensure the heart is functioning properly.
