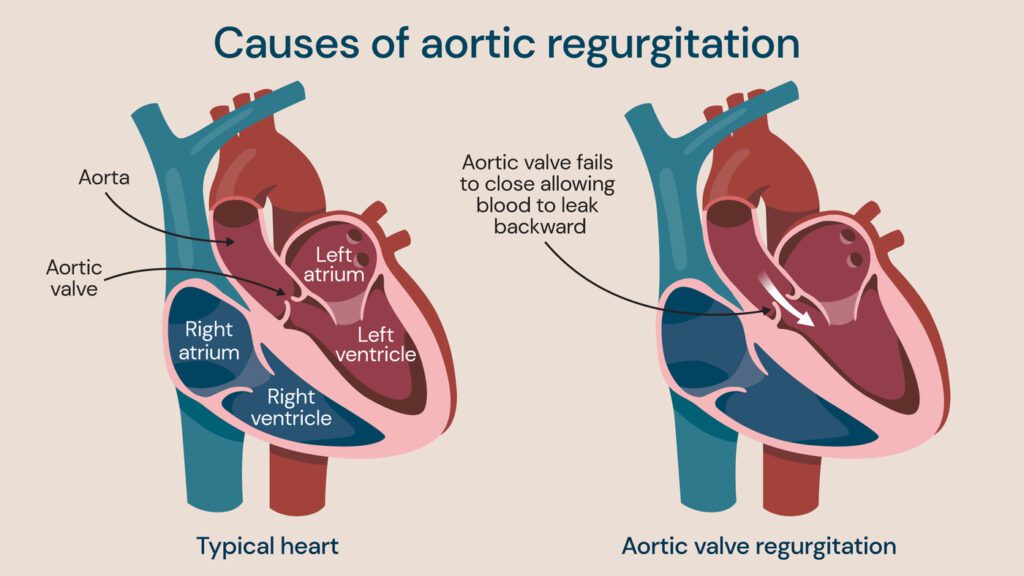
Another condition frequently encountered among aortic valve diseases is aortic valve insufficiency. In this disease, the aortic valve located between the left ventricle of the heart and the aorta does not close completely, causing some of the blood pumped from the heart to leak back. This situation leads to the heart working harder and, over time, causes the heart muscle to enlarge.
In this article, you can find all the details about aortic valve insufficiency, including its causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and modern treatment options.
What is Aortic Valve Insufficiency?
Aortic valve insufficiency is a condition where some of the blood leaving the heart returns due to incomplete closure of the aortic valve. This backflow increases the heart’s workload, and the heart begins to enlarge over time. As the disease progresses, signs of heart failure may appear.
It can occur alone or together with stenosis among aortic valve diseases.
What Causes Aortic Valve Insufficiency?
- Congenital Anomalies
- Structural abnormalities such as bicuspid aortic valve (two-leaflet valve) present from birth can lead to aortic insufficiency in some individuals.
- Rheumatic Fever
- Rheumatic fever disease experienced in childhood can cause deterioration of the aortic valve structure.
- Enlargement of the Aorta (Aortic Aneurysm)
- Enlargement of the aorta can disrupt the valve’s closing mechanism, leading to insufficiency.
- Connective Tissue Disorders
- Connective tissue disorders such as Marfan Syndrome and Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome predispose to the development of aortic valve insufficiency.
- Age-Related Changes
- As age progresses, calcification, reduced elasticity, and insufficiency can be seen in the aortic valve.
- Chest Trauma
- The aortic valve can be damaged as a result of traumatic injuries.
What Are the Symptoms of Aortic Valve Insufficiency?
It may not cause symptoms in mild cases. However, as the disease progresses, the following symptoms may be observed:
- Shortness of breath (especially with exertion)
- Feeling of fatigue
- Palpitations
- Irregular heart rhythm
- Chest pain
- Heart murmur
- Dizziness
- Fainting (in advanced cases)
How is Aortic Valve Insufficiency Diagnosed?
The most important method in diagnosing aortic valve diseases is echocardiography. This examination allows for detailed assessment of:
- The closing function of the aortic valve
- The amount of blood regurgitation
- The size of heart chambers
- The function of the heart muscle
is evaluated in detail.
If necessary, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), multi-slice computed tomography angiography, and cardiac catheterization provide valuable information in planning the treatment.
Aortic Valve Insufficiency Treatment Methods
The goal of treatment is to prevent heart enlargement. The choice of treatment is made based on the severity of the disease and the patient’s clinical condition.
Medication Treatment
Medication treatment is applied to patients with mild to moderate insufficiency who have no symptoms. Heart muscle supporting drugs and blood pressure regulators can be used. However, medication treatment does not completely eliminate the disease.
Surgical Aortic Valve Repair or Replacement
Surgical intervention is recommended for patients with advanced aortic valve insufficiency and impaired heart function.
Valve Repair
In some special cases, especially when the aorta is enlarged, valve repair is preferred. The valve’s own tissue is preserved.
Valve Replacement (AVR)
If the aortic valve cannot be repaired, it is removed and replaced with a mechanical or biological valve.
- Mechanical valve: It is more durable. However, the patient must use blood thinners for life.
- Biological valve: It does not require blood thinners, but has a limited lifespan.
Mini Aortic Valve Replacement
As an alternative to the classic surgical method, valve replacement can be performed with a small incision. The recovery period is shorter.
Sutureless Aortic Valve Replacement
It is a biological valve method that shortens the surgery time and is placed without using sutures.
TAVI Method
As in aortic valve stenosis, the aortic valve is replaced using the TAVI (Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation) method in some elderly patients. However, its application is limited in insufficiency cases.
In Which Cases Does Aortic Valve Insufficiency Require Surgery?
Surgical intervention is recommended in the following cases:
- Severe insufficiency
- Impairment of heart functions
- Left ventricular enlargement
- Significant complaints such as shortness of breath, fatigue
In aortic valve diseases, the most important criterion is to intervene before heart functions deteriorate.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is aortic valve insufficiency fatal?
If left untreated, it can lead to heart failure and serious deterioration in quality of life.
Does aortic valve insufficiency resolve on its own?
No. The progression of the disease cannot be stopped; medication can alleviate symptoms, but surgical intervention is the permanent solution.
Is it possible to live with aortic valve insufficiency?
While possible in mild cases, surgical intervention is essential in advanced cases.