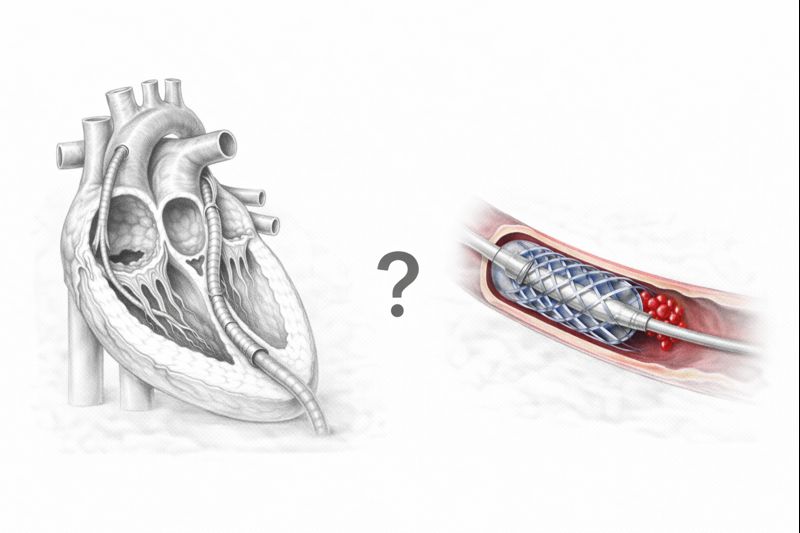
Coronary Bypass or Stent? This is one of the most critical questions for many patients diagnosed with coronary artery blockage, and the answer can vary depending on the individual.
Coronary artery disease is one of the most common cardiovascular diseases in the world and in our country, and it ranks high among the causes of death. The most important dilemma we face in treating this serious disease is: Should stent placement or coronary bypass surgery be preferred? The answer to this question may vary for each patient. Because one of the most fundamental principles in medicine is this: Every patient is different, so every treatment plan should be personalized.
What is a Stent? What is Coronary Bypass?
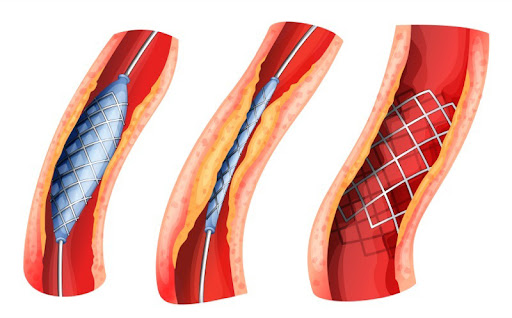
A stent is a device, usually in the form of a metal cage, applied to narrowed or blocked areas in the heart vessels. It aims to regulate blood flow by being placed inside the vessel during angiography. It is an interventional procedure performed without surgical incision.
In coronary bypass surgery, a ‘bridge’ is created to the area beyond the blocked vessel in the heart using a piece of vessel taken from another part of the body (usually from the leg or chest wall). Thus, blood flow to the heart is restored by bypassing the blockage.
Advancements in Stent Technology
Recent developments in stent technology have made it possible to use this method in wider patient groups. Especially with the use of drug-eluting stents, re-occlusion rates have been reduced and procedure success rates have increased. Today, many patients who would have undergone bypass surgery in the past can be successfully treated with the stent method.
However, this does not mean that stenting is the best option for every patient. In some special patient groups, coronary bypass surgery offers more long-term and permanent solutions compared to stenting.
Patient Groups Where Bypass Surgery is Recommended
Bypass surgery is more advantageous than stenting in the following situations:
- Diabetic patients: Research shows that bypass surgery extends life expectancy and reduces re-intervention rates in diabetic patients.
- Patients with blockages in two or more vessels: Surgery offers a more effective solution in individuals with multivessel disease.
- Main coronary artery (left main coronary artery) blockage: Surgery is usually prioritized for narrowing in this vital vessel.
- Patients who have previously had stents and developed re-occlusion: Bypass becomes a permanent solution in this case.
- Patients with weakened heart function after a heart attack: In this group, surgery is more beneficial for preserving heart function.
- Vessel structure unsuitable for stenting: Stent application does not yield good results in vessels with small diameters or long-segment narrowings.
Which Method is Safer?
Both methods have their own risks and advantages. Since stent procedure is less invasive, the hospital stay is shorter and the recovery process is faster. However, some patients have a risk of re-occlusion after stenting and the need for a second procedure.
Although bypass surgery is a larger operation, it offers a lower need for re-intervention in the long term. It can also have more pronounced positive effects on life expectancy and heart functions.
Personalized Treatment is Essential
A ‘one-size-fits-all solution’ approach is not possible in the treatment of coronary artery disease. The decision should be made based on the patient’s age, accompanying diseases, vessel structure, heart functions, and general health condition. A multidisciplinary approach, where cardiology and cardiovascular surgery specialists make a joint assessment, plays a critical role in determining the most appropriate treatment option.
If you have been diagnosed with coronary artery blockage, it is of great importance to decide on the most suitable treatment method for your personal health condition by obtaining different expert opinions. Remember, early diagnosis and correct treatment are everything for protecting your heart.